what happens to the energy of the universe during a physical or chemical process
3.ix: Free energy and Chemic and Concrete Change
- Folio ID
- 208094
Learning Objectives
- Define endothermic and exothermic reactions.
- Describe how heat is transferred in endothermic and exothermic reactions.
- Determine whether a reaction is endothermic or exothermic through observations, temperature changes, or an free energy diagram.
So far, we take talked nearly how free energy exists as either kinetic energy or potential free energy and how energy tin be transferred equally either heat or work. While it's important to understand the divergence between kinetic energy and potential energy and the difference between oestrus and work, the truth is, free energy is constantly changing. Kinetic energy is constantly being turned into potential energy, and potential energy is constantly existence turned into kinetic free energy. Likewise, free energy that is transferred as work might later end up transferred as heat, while energy that is transferred as estrus might later terminate up being used to do work.
Even though free energy tin can alter grade, it must still follow one fundamental law: Energy cannot be created or destroyed, information technology can only be changed from ane form to another. This law is known as the Law of Conservation of Free energy. In a lot of means, energy is like money. Y'all tin can exchange quarters for dollar bills and dollar bills for quarters, but no matter how oft yous convert between the two, you will not stop up with any more or any less money than you started with. Similarly, y'all can transfer (or spend) money using greenbacks, or transfer coin using a credit card; just you still spend the same amount of coin, and the store nevertheless makes the same amount of money.
A campfire is an example of basic thermochemistry. The reaction is initiated by the application of heat from a match. The reaction converting woods to carbon dioxide and water (amid other things) continues, releasing heat energy in the process. This heat free energy can then be used to melt food, roast marshmallows, or just continue warm when information technology'south common cold outside.
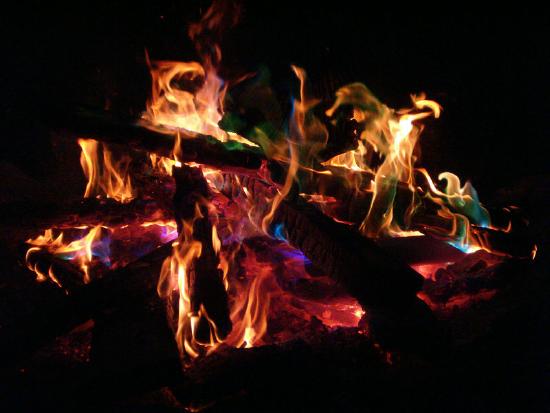

An paradigm of a campfire with colored flames, made by the burning of a garden hose in a copper pipe. (CC SA-BY 3.0; Jared)
Exothermic and Endothermic Processes
When physical or chemical changes occur, they are generally accompanied by a transfer of energy. The law of conservation of energy states that in any physical or chemical procedure, energy is neither created nor destroyed. In other words, the unabridged energy in the universe is conserved. In order to ameliorate understand the free energy changes taking place during a reaction, nosotros need to ascertain two parts of the universe:the organization and the surroundings. The system is the specific portion of matter in a given space that is being studied during an experiment or an observation. The surroundings are everything in the universe that is not part of the system. In practical terms for a laboratory pharmacist, the organisation is the detail chemicals beingness reacted, while the environment are the immediate vicinity within the room. During most processes, energy is exchanged between the system and the environs. If the system loses a certain amount of free energy, that same corporeality of energy is gained past the surround. If the system gains a certain corporeality of energy, that energy is supplied by the surround.
A chemical reaction or physical alter is endothermic if heat is absorbed by the system from the surround. In the class of an endothermic process, the system gains heat from the surroundings and and then the temperature of the surround decreases. The quantity of oestrus for a process is represented past the letter \(q\). The sign of \(q\) for an endothermic process is positive considering the system is gaining heat. A chemical reaction or physical alter is exothermic if heat is released by the organization into the environs. Considering the environment are gaining oestrus from the organization, the temperature of the surroundings increases. The sign of \(q\) for an exothermic procedure is negative considering the system is losing heat.
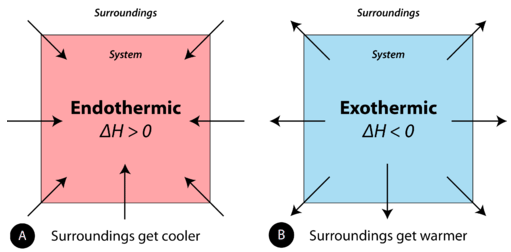
During stage changes, energy changes are ordinarily involved. For instance, when solid dry out ice vaporizes (physical alter), carbon dioxide molecules absorb energy. When liquid water becomes ice, energy is released. Recollect that all chemical reactions involve a change in the bonds of the reactants. The bonds in the reactants are cleaved and the bonds of the products are formed. Chemic bonds accept potential energy or "stored free energy". Because we are changing the bonding, this ways we are too irresolute how much of this "stored free energy" in that location is in a reaction.
Energy changes are often shown by drawing an free energy diagram. Energy diagrams prove the stored/hidden energy of the reactants and products as well as the activation free energy. If, on an free energy diagram, the products take more stored energy than the reactants started with, the reaction is endothermic. You lot had to give the reaction energy. If, on the energy diagram, the products accept less stored free energy than the reactants started with, the reaction is exothermic.
Example \(\PageIndex{1}\)
Characterization each of the following processes as endothermic or exothermic.
- water boiling
- gasoline called-for
- water ice forming on a pond
Solution
- Endothermic—you must put a pan of water on the stove and give information technology heat in order to get h2o to boil. Because yous are adding heat/energy, the reaction is endothermic.
- Exothermic—when yous burn something, it feels hot to you considering it is giving off heat into the environment.
- Exothermic—think of ice forming in your freezer instead. You put water into the freezer, which takes heat out of the water, to get it to freeze. Because heat is being pulled out of the water, it is exothermic. Rut is leaving.
Practice \(\PageIndex{1}\)
Label each of the following processes as endothermic or exothermic.
- water vapor condensing
- golden melting
- Answer (a)
- exothermic
- Answer (b)
- endothermic
Summary
Phase changes involve changes in energy. All chemical reactions involve changes in energy. This may be a change in estrus, electricity, light, or other forms of free energy. Reactions that absorb energy are endothermic. Reactions that release energy are exothermic.
Contributions & Attributions
This page was constructed from content via the following correspondent(due south) and edited (topically or extensively) past the LibreTexts development team to come across platform manner, presentation, and quality:
-
Marisa Alviar-Agnew (Sacramento City Higher)
-
Henry Agnew (UC Davis)
cooperhichislon75.blogspot.com
Source: https://chem.libretexts.org/Courses/Santa_Barbara_City_College/SBCC_Chem_101%3A_Introductory_Chemistry/03%3A_Matter_and_Energy/3.09%3A_Energy_and_Chemical_and_Physical_Change
0 Response to "what happens to the energy of the universe during a physical or chemical process"
Enviar um comentário